
In other words, differentiate a function to get its derivative, then differentiate again to get its second derivative. 2: Multi-Variable Calculus and Linear Algebra with Applications, 1 (2nd ed. When f is a function f(x) of a real variable x, and takes real, strictly positive values, this is equal to the derivative of ln(f), or the natural logarithm. A second derivative is found by differentiating a derivative of a function. 1: One-Variable Calculus with an Introduction to Linear Algebra, 1 (2nd ed.), Wiley, ISBN 978-5-1
#SECOND DERIVATIVE OF LOG X SERIES#
Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete and Impulsive Systems, Series A: Mathematical Analysis. "Extending the Algebraic Manipulability of Differentials".

Generalization to higher dimensions The Hessian In Leibniz notation:Ī = d v d t = d 2 x d t 2, įor other well-known cases, see Eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the second derivative. Inection Points Finally, we want to discuss inection points in the context of the second derivative. Roughly speaking, the second derivative measures how the rate of change of a quantity is itself changing for example, the second derivative of the position of an object with respect to time is the instantaneous acceleration of the object, or the rate at which the velocity of the object is changing with respect to time. So the second derivative of g(x) at x 1 is g00(1) 6¢1¡18 6¡18 ¡12 and the second derivative of g(x) at x 5 is g00(5) 6 ¢5¡18 30¡18 12: Therefore the second derivative test tells us that g(x) has a local maximum at x 1 and a local minimum at x 5. In calculus, the second derivative, or the second order derivative, of a function f is the derivative of the derivative of f. To find the derivative of other logarithmic functions, you must use the change of base formula: loga(x) ln(x)/ln(a). Differentiate using the Product Rule which states that is where and. Click on 'Draw graph' to display graphs of the function and its derivative. Find the 2nd Derivative yx natural log of x. Click on ‘Show a step by step solution’ if you would like to see the differentiation steps. These are called second partial derivatives, and the notation is analogous to the notation for. Its partial derivatives and take in that same two-dimensional input : Therefore, we could also take the partial derivatives of the partial derivatives. Also differentiation of a constant is always zero.The second derivative of a quadratic function is constant. Derivative of the function will be computed and displayed on the screen. Consider a function with a two-dimensional input, such as. We can commit a mistake in applying product rule by interchanging u and v in a hurry.

The derivative of a function, y f(x), is the measure of the rate of change.
#SECOND DERIVATIVE OF LOG X HOW TO#
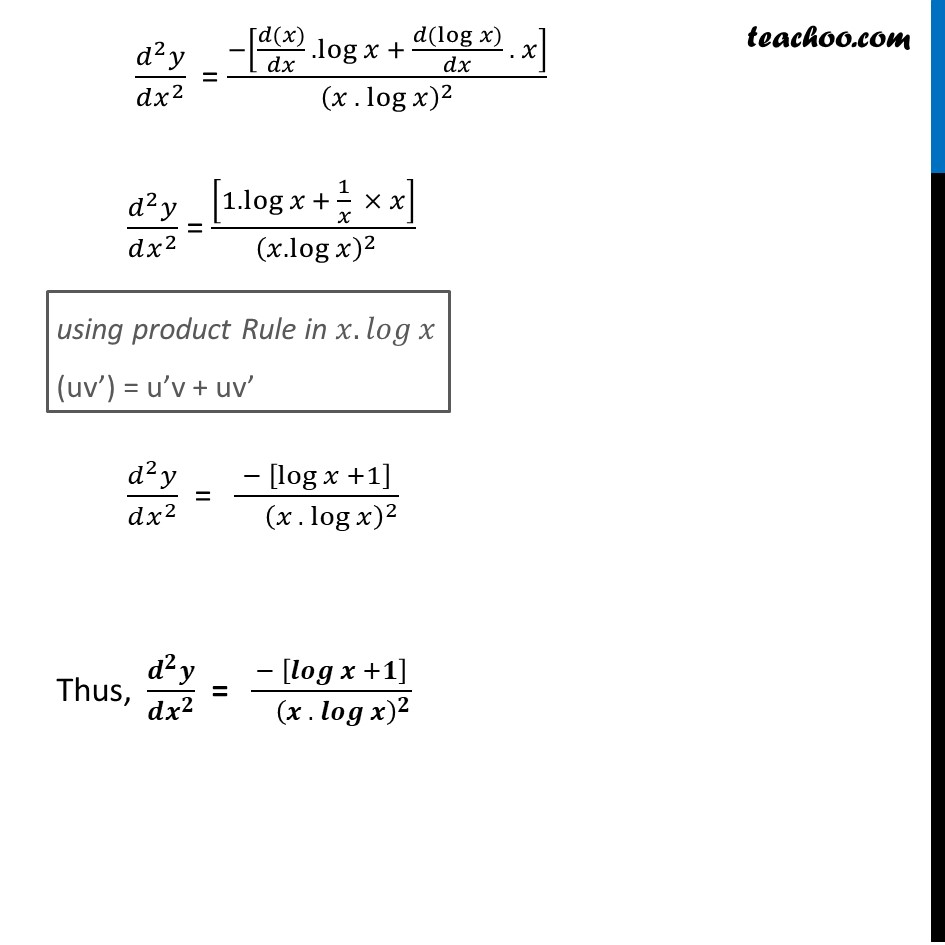
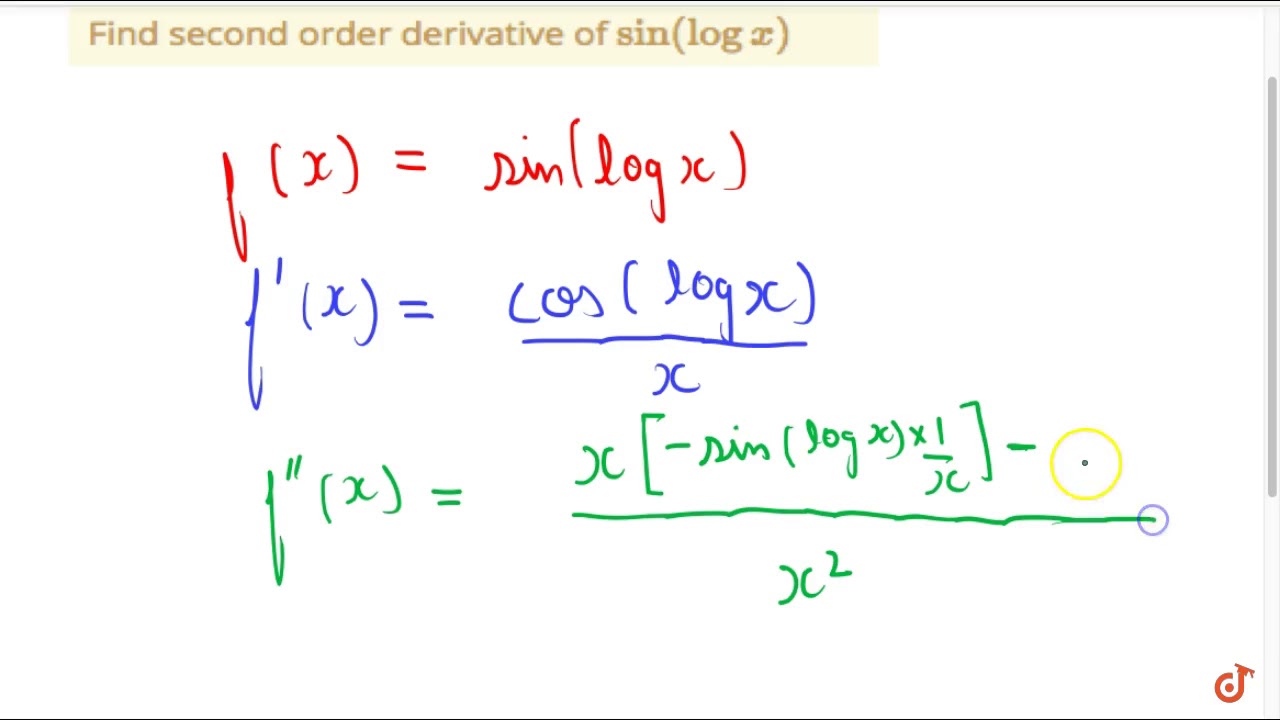
Also we need to remember the differentiation of x and log x. Learn how to find the derivative of exponential and logarithmic expressions. Note: We need to understand that derivative means differentiation. Product rule: If \ then its differentiation is \. The second-order derivatives are also used to get an idea of the shape of the graph for the given function. The derivative is used to measure the sensitivity of one variable (dependent variable) with respect to another variable (independent variable). The derivative is primarily used when there is some varying quantity, and the rate of change is not constant. Also we will be using the product rule of differentiation.ĭerivatives are defined as the varying rate of change of a function with respect to an independent variable. Here the second derivative has been asked which means we have to differentiate two times. Hint: Derivative means to differentiate the given term.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
